Source: securityboulevard.com – Author: Puja Saikia
Vulnerability-based attacks are growing. Undoubtedly, these attacks are hackers’ favorite ways to gain initial access. Such attacks rose by 124% in the third quarter of 2024 compared to 2023. Furthermore, the quick shot of hackers taking advantage of the security flaw (CVE-2024-5806) in Progress MOVEit Transfer amplifies the dreadfulness of unpatched vulnerabilities. Once the vulnerability was made public, it took them just hours to exploit them. Despite advanced cybersecurity, vulnerabilities that are not patched remain a major threat. As organizations adopt Artificial Intelligence, the Internet of Things, and remote work, managing and securing the expanding organizational platforms becomes harder. This widens the attack surface, giving hackers more entry points and thus, increasing risks. In 2025, prioritizing patch management is critical to avoid financial, operational, and reputational damage. Proactive protection is key as threats grow more sophisticated and this blog highlights the need to patch the vulnerabilities at the earliest.
Will Unpatched Vulnerabilities Persist in 2025 and Why?
If we look at the previous year’s statistics, vulnerabilities that are not patched will unfortunately endure as a major threat in 2025. On average, 115 CVEs were disclosed daily in the last quarter of 2024. The main reasons are the increasing intricacy of IT environments as well as the expanding attack surface. In 2024, attacks on known vulnerabilities surged by 54% compared to the previous year, reflecting the need to patch vulnerabilities faster. Despite this, 56% of older vulnerabilities are still an active target for hackers.
Even critical vulnerabilities often go unpatched, with 32% remaining exposed for over 180 days. The long lifecycle of breaches further multiplies the issue. It takes an average of 204 days to detect a breach and 73 days to contain it. The timeline is based on 2024. Thus, without proactive measures, unpatched vulnerabilities will continue to be a primary gateway for cyberattacks in 2025, stressing the critical need for timely patch management and real-time threat monitoring.
A few of the many issues that contribute to these include –
Increasing Sophistication in IT Ecosystems
The modern IT infrastructure is made up of not a single software but a mix of traditional software, cloud services, and IoT or smart devices. Each part requires its respective updates and such updates have no fixed time. Therefore, it becomes difficult and time-consuming on the part of IT teams to manage all these patches and keep the IT ecosystem smooth and secure.
Resource Constraints
Another reason why unpatched vulnerabilities prevail is due to resource and time constraints. Small organizations often lack the required skilled workers to keep up with the regular software updates. In the case of larger organizations, delays in patching can be the result of limited budgets or attending to more priority tasks. In this way, updates are delayed which opens up the scope for hackers to exploit the un-updated organizational assets, applications, etc that are now vulnerable.
Patch Fatigue
Patch Fatigue is a term used to describe the difficulty of IT teams to manage software updates when there are many updates in line. Such a large influx of updates can lead to missed updates or cause delays in updating them. In cases, where updates are prioritized in terms of urgency, the updates that are put off create security gaps that hackers can exploit.
Zero-Day Exploits
Zero-day exploits are flaws in software that are not known and no fix has been found yet. Hackers can find and use these flaws, called zero-day vulnerabilities, faster than the company can create a fix. These vulnerabilities can stay a threat for up to 2 years because patches often take too long to be applied.
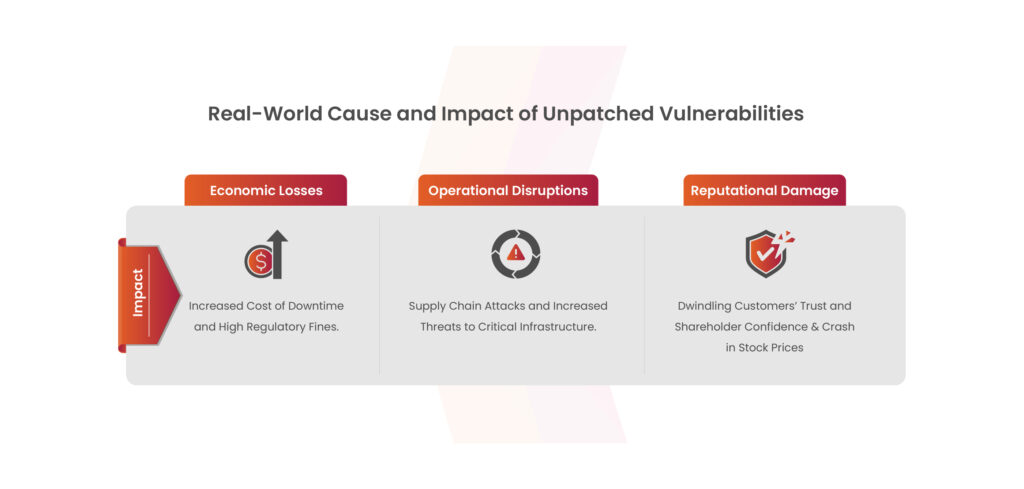
The impact if the vulnerabilities are not patched will differ from industry to industry. However, the three most dreadful impacts that will leave a serious mark on the affected organization are –
- Economic Losses
- Operational Disruptions
- Reputational Damage
Real-Time Attacks and Lessons Learned
Attack 1: Equifax Breach (2017)
Attack Summary: – A major data breach due to an unpatched vulnerability. It resulted in the loss of personal data of 147 million customers followed by reputational and financial loss.
Lessons Learned: Organizations must regularly conduct Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT). As because, it is an integral part of vulnerability management and regular patching is a must.
Attack 2: WannaCry Attack (2017)
Attach Summary: A ransomware attack where hackers exploited an unpatched vulnerability in Microsoft Windows. Lakhs of computers across 150+ countries were affected.
Lessons Learned: Organizations must regularly update their software and emphasize applying security patches regarding known vulnerabilities as and when found.
Attack 3: Colonial Pipeline Attack (2021)
Attack Summary: A ransomware attack where hackers shut down the pipeline by exploiting a VPN system. Moreover, it led to a shortage of fuel and price spikes.
Lessons Learned: Organizations must secure remote access points, fix unpatched vulnerabilities, and have strong incident response plans for responding to breaches and backing up data.
Book a Free Consultation with our Cyber Security Experts

Industries at Greatest Risks from Unpatched Vulnerabilities in 2025
Almost all industries are prone to the risks associated with unpatched vulnerabilities. However, analyzing the previous trends on the same, certain industries are at a higher risk due to their nature of operations and the sensitivity of the data they handle.
- Healthcare:
Almost every medical device is connected to the internet (IoT devices). If such devices are not properly secured and updated, hackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to steal patient data or even disrupt life-saving equipment which could have serious consequences.
- Finance:
Financial institutions are the prime targets for hackers. They target these industries, especially for spying and fraud. Vulnerabilities in this industry are found in its banking systems, mobile apps, and payment platforms. If remain unpatched, these could allow hackers to steal money, access confidential data, and cause financial instability.
- Manufacturing:
Manufacturing industries are constantly using Operational Technology (OT) to control their machinery and production lines. If these hardware and software are not patched, they can be vulnerable to cyberattacks. Other consequences that the industry can face once their OT security is breached include production halts, equipment damage, or even safety issues for workers.
- Public Sector:
Most of the critical infrastructures that are highly targeted fall under the government. Among the critical infrastructure, power grids, transportation, and communication networks are highly targeted. If hackers exploit vulnerabilities that are not patched, it can lead to widespread disruptions and even cause threats to national security.
How to Mitigate Unpatched Vulnerabilities in 2025?
Before we dive into the ways, let’s have a look at some of the figures that highlight the importance of mitigating the vulnerabilities:
Organizations that contained breaches within 200 days saved over $1 million. Through the use of virtual patches, organizations were able to block 71% of API attacks and 62% of attacks on the web in 2024. The usage of vulnerability scanners with Web App and API Protection (WAAP) solutions reduced patch remediation times from months to just 3 days.
Automate Updation
Organizations need to prioritize high-risk patches first. It can be done using tools available to automate updates and identify critical vulnerabilities so that vulnerabilities can be patched at the earliest.
Improve Monitoring and Detection
It is important for organizations to continuously monitor for unusual activities along with unpatched vulnerabilities. Advanced threat detection mechanisms like EDR and SIEM can be used for this purpose.
Network Segmentation
Organizations to ensure that no vulnerabilities prevail in their network need to divide their network into segments. It will help limit the spread of any attack in case of vulnerability exploitation. Also, it is important to adopt a zero-trust approach, verifying every access request.
Regular Vulnerability Scanning
Organizations should continually scan for vulnerabilities in their applications and other platforms for unpatched vulnerabilities. It can be done by conducting VAPT. Assessing third-party vendors for security gaps is also recommended.
Governance and Compliance
Organizations must comply with relevant security standards and get audits done regularly. It is also important to regularly check if the patch management policies are being followed to avoid fines and penalties.
Backup and Recovery
Organizations must regularly back up critical data. Furthermore, ensure that backups are stored securely. Apart from proper backup, organizations with a disaster recovery plan in place help restore systems quickly if an attack occurs.
How Kratikal Can Help Detect Unpatched Vulnerabilities?
Around 1/4th of breaches are linked to vulnerabilities in applications and stolen credentials. Therefore, it is important that organizations secure their applications in today’s digitally advanced environment. Kratikal is known for its robust cybersecurity solutions.
Being a CERT-In Empanelled Auditor, Kratikal can help organizations get their compliance audit done which will help them save from any economic losses like regulatory fines. Also, vulnerabilities can be identified by conducting regular vulnerability assessment and penetration testing (VAPT) as part of the vulnerability management process. From web and mobile application security testing, network security testing, IoT security testing, and OT security testing for manufacturing to medical devices security testing for the healthcare industry, Kratikal can help organizations identify vulnerabilities and send patching recommendations.
Also, Kratikal’s VMDR and pentest tool, AutoSecT, can help scan and identify vulnerabilities in four platforms – Web App, Mobile App, Cloud, and API in a single dashboard. Kratikal can also help organizations in Incident Response Planning by making a clear plan for responding to breaches, moreover, using its threat intelligence services to keep organizations updated on emerging threats.
Unpatched vulnerabilities can be described as an open invitation for hackers to your organization, the cost of which is heavier in the pockets than one can imagine!
FAQs
- What are unpatched vulnerabilities?
Unpatched vulnerability refers to a security flaw or loophole present in the organization’s assets or applications that are not yet patched or updated. These unpatched vulnerabilities can be exploited by hackers who are looking to gain access to the organization.
- What is the potential risk of an unpatched software vulnerability?
An unpatched software vulnerability can lead to serious risks like economic losses caused by downtime costs, regulatory fines, etc. It also leads to operational disruptions, for example, an organization’s critical infrastructure being attacked through supply chain attacks. Moreover, reputational damage is a common potential risk across all industries.
The post Impact of Unpatched Vulnerabilities in 2025 appeared first on Kratikal Blogs.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Kratikal Blogs authored by Puja Saikia. Read the original post at: https://kratikal.com/blog/impact-of-unpatched-vulnerabilities-in-2025/
Original Post URL: https://securityboulevard.com/2024/12/impact-of-unpatched-vulnerabilities-in-2025/
Category & Tags: Security Bloggers Network,CERT-In,Cyber awareness,Cyber Security,cyber security services,VAPT,VAPT services – Security Bloggers Network,CERT-In,Cyber awareness,Cyber Security,cyber security services,VAPT,VAPT services
Views: 6




















































