Source: heimdalsecurity.com – Author: Andra Andrioaie
Identity and access management is a key component in ensuring the security of data. It can be used to protect companies against data breaches by providing a layer of security that protects information from unauthorized access. Find more about this concept along with why IAM is important and what is the best approach when implementing it.
What Is IAM?
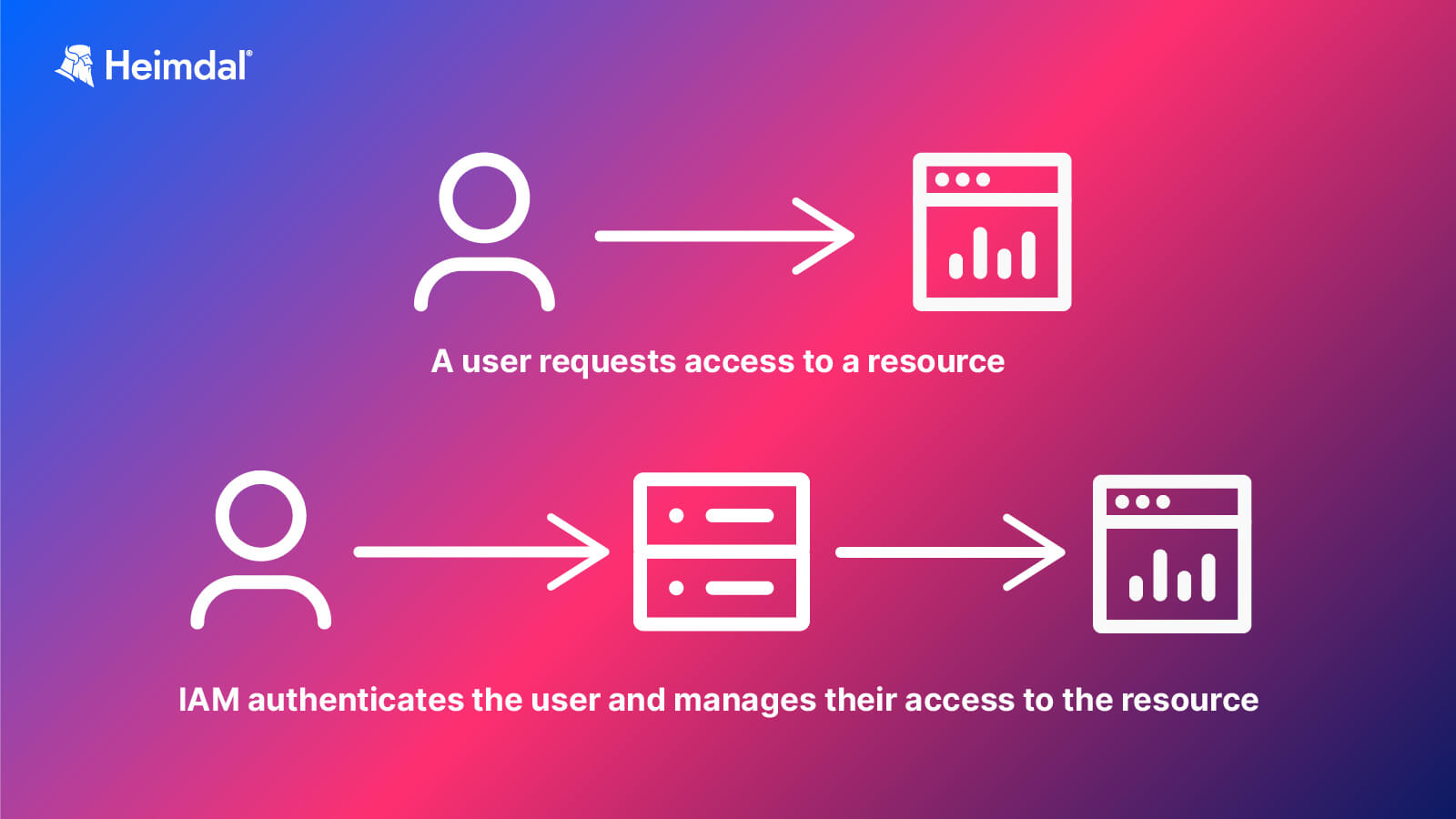
Identity and access management, often abbreviated as IAM, is a set of policies, processes, and technologies that help organizations manage the identities of individuals and devices, authenticate these identities for access to data or other resources, and monitor who has accessed what.
How Does Identity and Access Management Work?
Through an identity and access management system, IT teams can properly control user access to critical data. The identity and access management framework of technologies works by providing the data on how individuals and their roles are identified in a system and what criteria are used to link these roles with users. It also supports the removal, addition, and update of users and roles, the distribution of access levels, and the management of user identities ’database.
How Are IAM Systems Deployed?
Identity and Access Management systems can be delivered through various means. Here are they:
- on-premises;
- the cloud – by means of a third-party vendor;
- through a hybrid model.
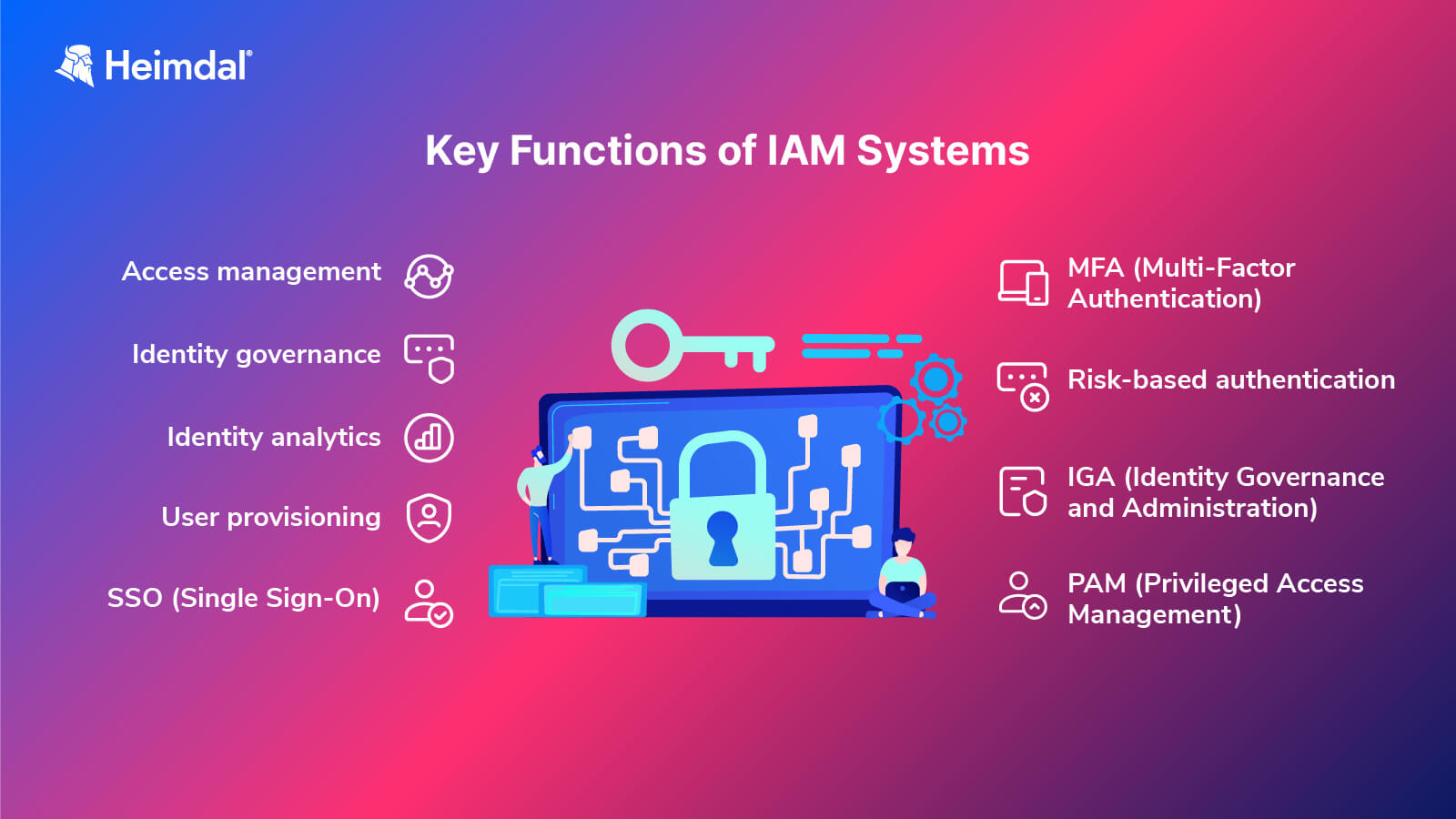
Key Functions of Identity and Access Management Systems
- Access management: these encompass access policies that use SSO (single sign-on) and MFA (multi-factor authentication);
- Identity governance: this has the role of user account lifecycle management, focusing on elements such as provision and entitlements related to those accounts;
- Identity analytics: this IAM function works on the identification and consolidation of credential management;
- User provisioning: this feature focuses on creating and assigning new user accounts automatically;
- SSO (Single Sign-On): this function makes it easier for users to access services because it allows them to consolidate their passwords and credentials into a single account with robust password protection;
- MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) involves access control made up of many steps to properly assess the users’ authenticity and thus works on dramatically decreasing the risk of credential theft;
- Risk-based authentication: this is a type of authentication that employs different algorithms that calculate how users’ actions might involve a potential risk. If some actions are scored as high-risk, these will be both blocked and reported;
- Identity governance and administration (IGA): this function focuses on the control of entitlements which helps reduce the risk posed by privileged access or excessive access in general;
- PAM (Privileged Access Management): PAM might be sometimes confused with IAM. However, the basic difference between them is that IAM takes care of the management of all users’ accounts, while Privileged Access Management focuses only on privileged accounts, so it is a category of IAM.
Identity and Access Management Concepts
When you look for the phrase “identity and access management” you might find throughout your search some other related concepts. Let’s shed some on the main IAM related terms:
- Authentication: as the very name says, this has the role to authenticate users, services, and applications, so basically to check their identity;
- Authorization: this concept defines how access is granted to the above instances to different resources;
- Biometric authentication: biometrics are used in modern IAM systems to provide more precise authentication. They capture fingerprints, irises, faces, palms, gaits, voices, and, in certain circumstances, DNA, among other biometric features;
- Provenance: a digital signature or an attestation record is used to check the identity or the authentic nature of an image or piece of code;
- Behavioral authentication: when dealing with highly sensitive information and systems, companies have the option to implement behavioral authentication, which involves analyzing keyboard dynamics or mouse-usage patterns in order to obtain more comprehensive information.
- Active Directory (AD): AD, developed by Microsoft, is a directory service for user identity for Windows domain networks. Despite being proprietary, AD is integrated into most Windows Server operating systems, hence being widely used;
- Context-aware network access control:context-aware network access control is a policy-driven approach that allows or denies access to network resources based on the user’s current context. For instance, if a user tries to authenticate from an IP address that is not on the whitelist, access will be denied;
- De-provisioning:this process entails revoking or deleting a user’s access to applications and systems and usually happens when an employee leaves the organization or when access is no longer needed;
- Identity as a Service (IDaaS): Identity as a Service (IDaaS) is a cloud-based solution for Identity and Access Management (IAM), in which access and identity services are provided over the internet, rather than on-premises;
- Identity lifecycle management: just like access lifecycle management, this concept encompasses the entire range of procedures and technologies employed to maintain and update online identities. The concept covers identity synchronization, provisioning & de-provisioning, and continuous management of user characteristics, credentials, and permissions;
- User behavior analytics (UBA):UBA systems monitor user behavior patterns and automatically employ algorithms and analysis to find significant anomalies that may suggest possible security risks;
IAM Benefits for Organizations
There are numerous advantages associated with implementing identity and access management (IAM) solutions in a business environment. The benefits mentioned below outline specific areas that make IAM an excellent investment.
It Eliminates Human Error through Automation and Granular Control
If you run a company or work in the IT department, you know that you have to deal with lots of rules to properly secure access to corporate resources. This means human error should be out of the question. Identity access management helps implement access controls at a granular level through automation of these tasks. Automation also saves you money, effort, and time you usually spend on manually managing all these accesses. This applies to both on-premises and cloud resources.
Improved Business Operational Performance
With IAM put in place, businesses do not need to worry about inefficient overall operational performance, and that it’s because it provides an easier way to implement policies surrounding user privileges, user authentication, and validation, and handling potential issues caused by privilege creep.
Through identity and access management automated workflows are created. So, if there’s a new hire situation or even a role transition happening in your company, IAM makes the process smooth improving also the processing time meant for these kinds of identity changes.
What’s more is that IAM solutions restrict abnormal behavior using technologies like machine learning, artificial intelligence, and risk-based authentication.
It Secures Your Business
Another benefit of identity and access management is that it efficiently secures your business. The granular control I was talking about above also helps significantly decrease the potential data breaches that might be caused by malicious insiders, as IAM works using the principle of least privilege, restricting users’ access only to areas and resources they specifically need for an assigned task. This means that privilege escalation cannot happen without being noticed.
However, not only insider threats are kept away, but also external threats that cannot so easily penetrate your network since so many access controls should be bypassed.
IAM Works to the Benefit of the Users Supporting Productivity
Identity and access management eliminates the headaches that end-users, system admins, or even application owners face when they should sign up or sign in.
For instance, through SSO joined by adaptive MFA, users are provided with more rapid and facile access to resources they need to access, so the overall user experience is definitely enhanced. Besides, through passwordless authentication, users get rid of the hassle of keeping track of the multiple passwords they need along the way.
What’s more is that customers, partners, contractors, and suppliers can access a company’s network through mobile apps, on-premises apps, and SaaS without compromising security thanks to IAM technologies, improving thus the collaboration component.
Regulatory Compliance
Identity and access management systems assist businesses in complying with regulatory bodies by allowing them to demonstrate that company data is safe and sound, so thus it is not being exploited. Besides, another advantage would be that if they meet compliance, companies might ensure data availability for audit purposes when necessary.
What are some data protection standards? We can mention a few: GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) which everybody knows, HIPAA, NIST, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, and so on. So basically, when audit time knocks on your door you can prove administrative transparency easy and quick, this also being a contributing factor too to the reliability of your business.
Reduced Operational Costs
If you use cloud-based IAM services, you can reduce the costs driven by on-premise infrastructure maintenance, thus letting you invest your money more wisely.
Besides, it says no more to password resets. Reportedly, there’s a 50 % that links IT help desk calls to password resets, because, guess why? With so many places to authenticate, people forget their passwords. Not to mention that businesses have to shell out on an average $70 for a password reset. With IAM you rely less on passwords.
Say Goodbye to the Hassle of Weak Passwords
Weak passwords become one of the weakest links and an obvious path for hackers who intend to infiltrate your network and cause data breaches. Through IAM, users will be prevented to use passwords that are not strong enough and will ensure these are changed on a regular basis.
Identity and Access Management Risks
The implementation of identity and access management can face many challenges and here are some:
- properly providing initial access to a new hire/contractor/service/app;
- properly reducing or removing access rights;
- the correct identification of dormant accounts that might pose security risks;
- another significant problem when adopting an IAM platform is maintaining trust connections after access has been granted;
- any IAM solution must also work in tandem with the organization’s single sign-on (SSO) strategy. What this means is that the SSO platform should make it simple to gain safe access to a company’s entire app range, whether they’re hosted on-premises or in the cloud.
What Are Some IAM Technologies?
Since IAM systems should have the capacity to integrate with other systems, here are the three main technologies these tools should support:
Security Access Markup Language (SAML)
SAML stands for an open standard that allows an identity provider system, such as an IAM, to exchange authentication and authorization information with a service or application.
OpenID Connect (OIDC)
OIDC makes part also of the category of open standards, which has the capacity to allow users to log into their applications using an identity provider. Even if it shows similarities with the above-mentioned Security Access Markup Language, however, the main difference between them is that the first is based on the OAuth 2.0 standard sending data in JSON rather than XML, as SAML does.
System for Cross-Domain Identity Management (SCIM)
SCIM is the abbreviation for System for Cross-domain Identity Management and represents a standard that allows two systems to automatically share identity information. Despite the fact that both SAML and OIDC can send identity information to an application during the authentication process, SCIM is employed for updated user data maintenance purposes in situations like:
- a new user is assigned to a service or app;
- user data modification takes place;
- process of termination of users is put in place.
Identity and Access Management Best Practices
Enforcing best practices for identity and access management (IAM) empowers you to have visibility into who has access to sensitive data and the specific conditions under which they can access it. Here is a list of some of the most important Identity and Access Management best practices that every organization should follow:
- Consider an RBAC approach
- Implement a lifecycle management solution
- Start with an audit of existing and legacy systems
- Implement Zero-trust security
- Use multi-factor authentication
- Enforce a strong password policy
Keep an eye on the blog for the upcoming extensive article that will include additional best practices and a detailed analysis of each one of them.
How Can Heimdal® Help?
Integrate Privileged Access Management within your IAM strategy
Due to the evolution and growth of the “work from home” approach, more and more users are granted privileges because they need different accesses to perform their jobs, so these privileges are no longer limited solely to IT administrators, as anybody can now become a privileged user. That’s why the necessity to integrate an efficient Privileged Access Management approach into an Identity and Access Management Strategy has become more and more self-understood.
Since privileged accounts have special permissions and are the ones close to the most critical data of an organization, they, of course, require special attention and management that only can be acquired through a powerful PAM strategy powered by an automated Privileged Access Management Solution that will properly manage the approval/denial flow to privileged sessions.
A PAM solution will enforce the principle of the least privilege and here’s the benefit of it being integrated with IAM: this ensures that only the appropriate users, who can prove their identities via IAM, have access to the right systems, which are managed by PAM solutions.
System admins waste 30% of their time manually managing user
rights or installations
Heimdal® Privileged Access
Management
Is the automatic PAM solution that makes everything
easier.
- Automate the elevation of admin rights on request;
- Approve or reject escalations with one click;
- Provide a full audit trail into user behavior;
- Automatically de-escalate on infection;
Why Choose Heimdal Privileged and Access Management?
The Heimdal Privileged and Access Management solution is great for many reasons, but here are the most important ones:
- it supports PEDM-type (Privilege Elevation and Delegation Management) non-privileged user account curation functionalities for AD (Active Directory), Azure AD, or hybrid setups, thus removing the risk posed by over-privileged accounts;
- it gives you power over what happens during an elevated session and stronger security against insider threats;
- if paired with our Next-Gen Antivirus & MDM, it automatically deescalates user permissions on threat detection;
- it gives you flexibility in the approval/denial flow since you can grant or revoke permissions from anywhere in the world;
- it supports Zero-Trust execution;
- it supports just-in-time access: the privileged session has a limited timeframe, dramatically reducing this way the time an attacker would have to move laterally across the network if he had previously managed to get access to a privileged account;
- you can remove local admin rights using Heimdal PAM closing off OS and web vulnerabilities this way;
- you can prove compliance with NIST AC-5 and NIST AC-1,6.
What’s more is that it works even better when paired with Heimdal Application Control, a solution that allows you to whitelist or blacklist applications based on file path, publisher, certificate, vendor name, software name, MD5, and more, protecting thus your critical business assets.
See for yourself the quality that Heimdal’s PAM brings to the table by booking a demo or contacting us at sales.inquiries@heimdalsecurity.com!
Wrapping Up
You now understand why Identity and Access Management plays a major role in securing and properly assessing the individuals’ identities within an organization. Now it’s time to implement it if you haven’t done it yet!
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Youtube, for more cybersecurity news and topics.
Last updated by Antonia Din.
Original Post URL: https://heimdalsecurity.com/blog/identity-and-access-management-iam/
Category & Tags: Access Management,Cybersecurity Basics,PAM – Access Management,Cybersecurity Basics,PAM