A new Python-based credential harvester and SMTP hijacking tool named ‘Legion’ is being sold on Telegram that targets online email services for phishing and spam attacks.
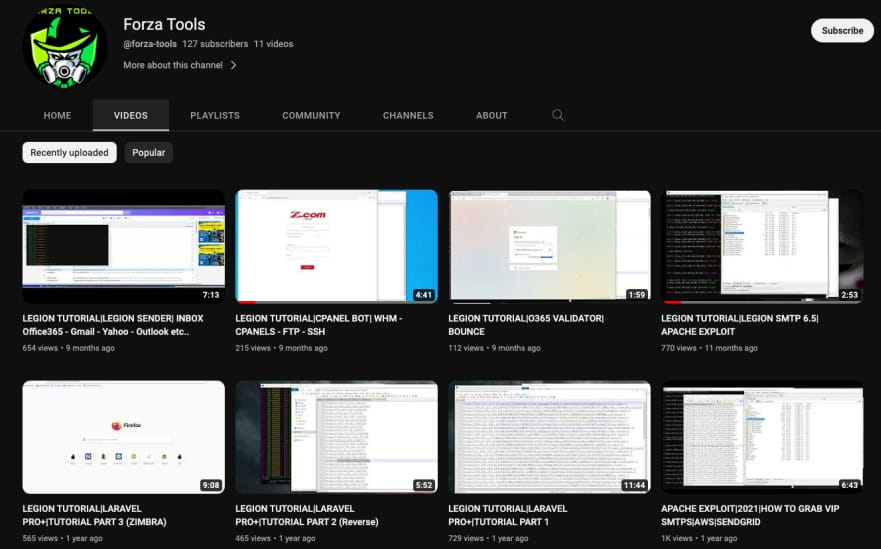
Legion is sold by cybercriminals who use the “Forza Tools” moniker and operate a YouTube channel with tutorials and a Telegram channel with over a thousand members.
Legion is modular malware which, according to Cado, is likely based on the AndroxGhOst malware and features modules to perform SMTP server enumeration, remote code execution, exploit vulnerable Apache versions, brute-force cPanel and WebHost Manager accounts, interact with Shodan’s API, and abuse AWS services.
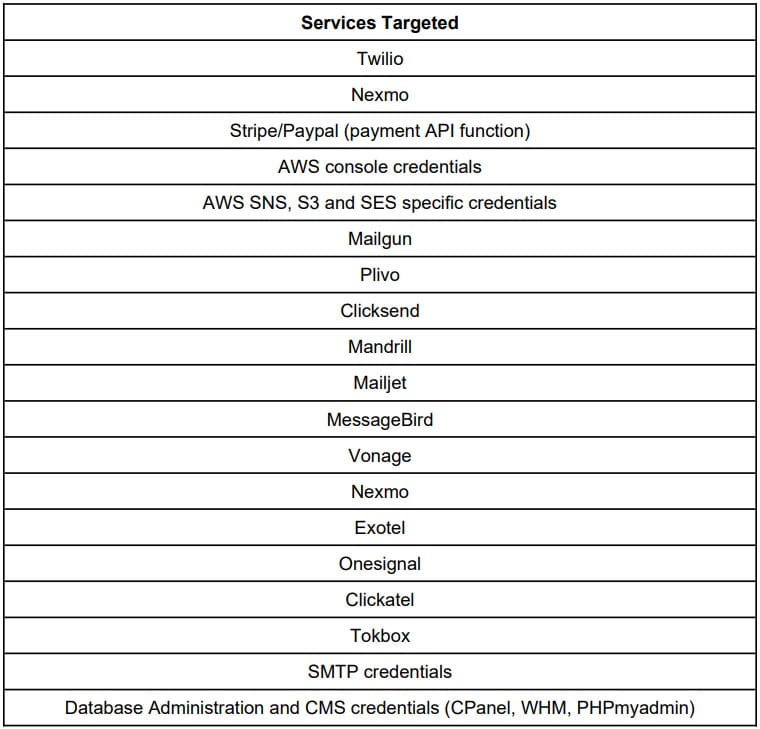
The tool targets many services for credential theft, including Twilio, Nexmo, Stripe/Paypal (payment API function), AWS console credentials, AWS SNS, S3 and SES specific, Mailgun, and database/CMS platforms.
Apart from extracting credentials and breaching web services, Legion can also create administrator users, implant webshells, and send out spam SMS to customers of U.S. carriers.
Harvesting credentials
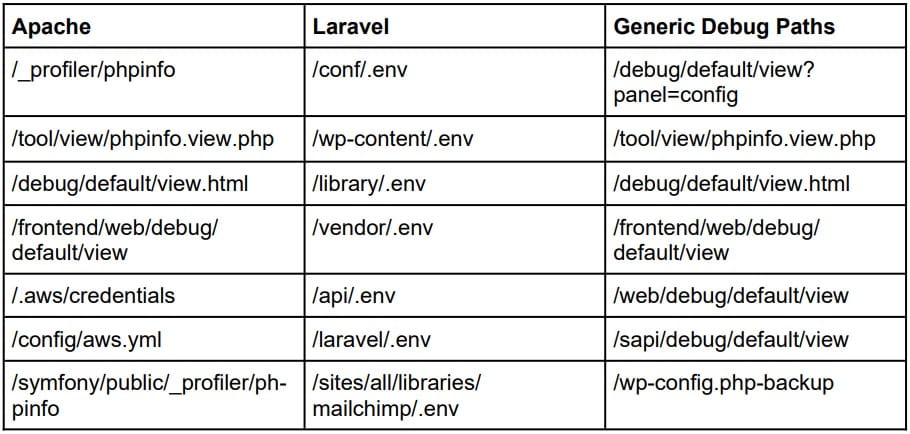
Legion generally targets unsecured web servers running content management systems (CMS) and PHP-based frameworks like Laravel by using RegEx patterns to search for files commonly known to hold secrets, authentication tokens, and API keys.
The tool uses an array of methods to retrieve credentials from misconfigured web servers, like targeting environment variable files (.env) and configuration files that might contain SMTP, AWS console, Mailgun, Twilio, and Nexmo credentials.
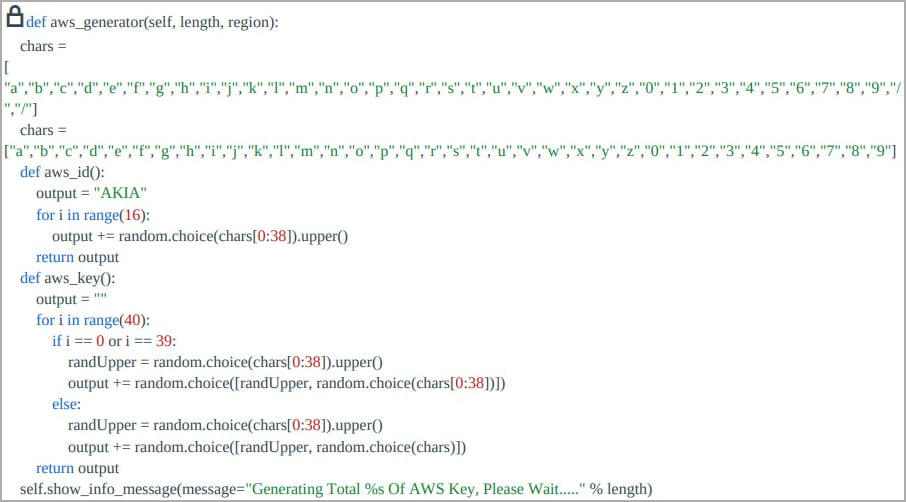
Besides attempting to harvest AWS credentials, Legion also features a brute-forcing system to guess them.
However, Cado comments that it is statistically unlikely that this system can generate usable credentials in its current state. A similar feature is included for brute-forcing SendGrid credentials.
Regardless of how the credentials are obtained, Legion will use them to gain access to email services and send out spam or phishing emails.
If Legion captures valid AWS credentials, it attempts to create an IAM user named ‘ses_legion,’ and sets the policy to give it administrator rights, giving the rogue user full access to all AWS services and resources.

Legion can also send SMS spam by leveraging stolen SMTP credentials after generating a list of phone numbers with area codes retrieved from online services.
The carriers supported by the malware include AT&T, Sprint, US Cellular, T-Mobile, Cricket, Verizon, Virgin, SunCom, Alltel, Cingular, VoiceStream, and more.
Finally, Legion can exploit known PHP vulnerabilities to register a webshell on the targeted endpoint or perform remote code execution to give the attacker full access to the server.
In conclusion, Legion is an all-purpose credential harvester and hacking tool gaining traction in the world of cybercrime, increasing the risk for poorly managed and misconfigured web servers.
AWS users should look for signs of compromise, like changing the IAM user registration code to include an “Owner” tag with the value “ms.boharas.”