Winter Vivern (aka TA473), a Russian hacking group, has been exploiting vulnerabilities (CVE-2022-27926) in unpatched Zimbra instances to access the emails of NATO officials, governments, military people, and diplomats.
The CVE-2022-27926 flaw affects versions 9.0.0 of Zimbra Collaboration, which is used to host webmail portals with public access. The attackers can also exploit compromised accounts to conduct lateral phishing attacks and further infiltrate the target companies.
Since at least February 2023, TA473 has targeted US political officials and personnel. The threat actors developed bespoke JavaScript payloads for the webmail portals of each government target.
Researchers have observed TA473, a newly minted advanced persistent threat (APT) actor tracked by Proofpoint, exploiting Zimbra vulnerability CVE-2022-27926 to abuse publicly facing Zimbra hosted webmail portals. The goal of this activity is assessed to be gaining access to the emails of military, government, and diplomatic organizations across Europe involved in the Russia Ukrainian War.
The cyber actions of TA473 align with the support of Russian and/or Belarussian geopolitical aims.
JavaScript Payloads Modified to Steal Credentials
The JavaScript payloads were designed to conduct Cross Site Request Forgery attacks and steal usernames, passwords, as well as store active session and CSRF tokens from cookies to facilitate the login to webmail portals accessible to the public.
These payloads enable actors to steal usernames, passwords, and active session and CSRF tokens from cookies that allow login to susceptible webmail portals of target organizations that are accessible to the public, explains Security Affairs.
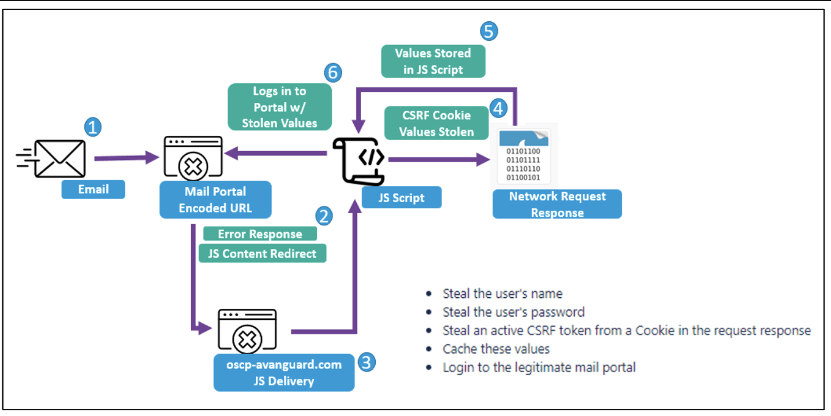
To detect unpatched webmail platforms used by target firms, the APT group employs scanning technologies like as Acunetix. The threat actors send phishing emails using a hacked address that has been faked to look like someone from their organization.
Once the susceptible platform has been determined, the attackers send phishing emails containing malicious URLs that exploit a known vulnerability to run JavaScript payloads within the victim’s webmail portals.
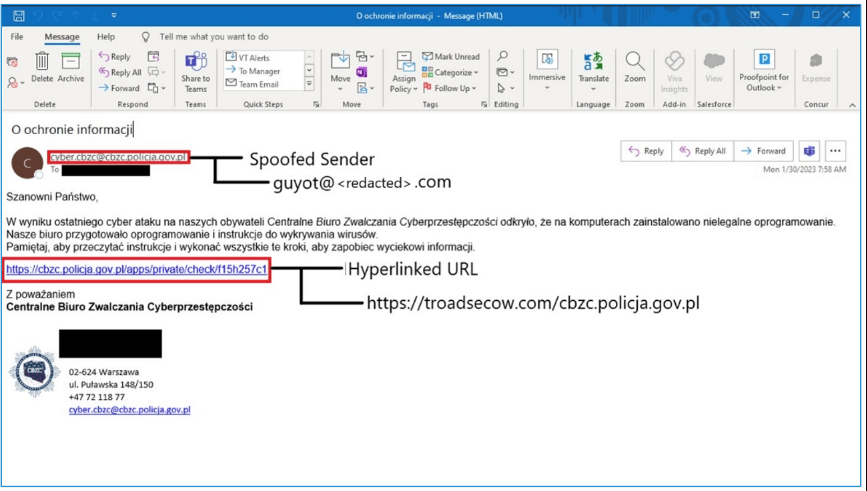
Proofpoint discovered many samples of modified CSRF JavaScript payloads delivered via both the CVE-2022-27926 bug and prior delivery methodologies used by the APT organization.
These CSRF JavaScript code blocks are executed by the server that hosts a vulnerable webmail instance. (…) Further, this JavaScript replicates and relies on emulating the JavaScript of the native webmail portal to return key web request details that indicate the username, password, and CSRF token of targets. In some instances, researchers observed TA473 specifically targeting RoundCube webmail request tokens as well.
The experts conclude that TA473’s persistent approach to vulnerability scanning and exploitation of unpatched vulnerabilities hitting publicly facing webmail sites is a crucial component in this actor’s success (IOCs). TA473 spends time and resources to compromise specific entities with unique JavaScript payloads for the targeted webmail portal.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube for more cybersecurity news and topics.
If you liked this post, you will enjoy our newsletter.
Get cybersecurity updates you’ll actually want to read directly in your inbox.