Source: securelist.com – Author: AMR
Since the beginning of the year, we’ve been tracking in our telemetry a new wave of DCRat distribution, with paid access to the backdoor provided under the Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) model. The cybercriminal group behind it also offers support for the malware and infrastructure setup for hosting the C2 servers.
Distribution
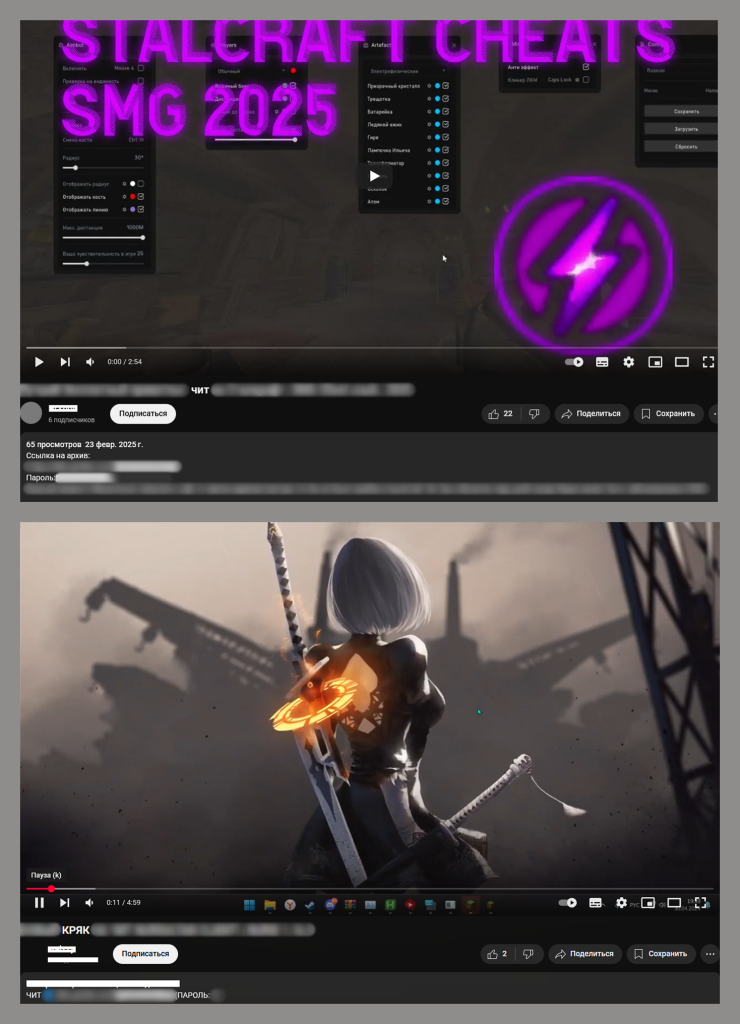
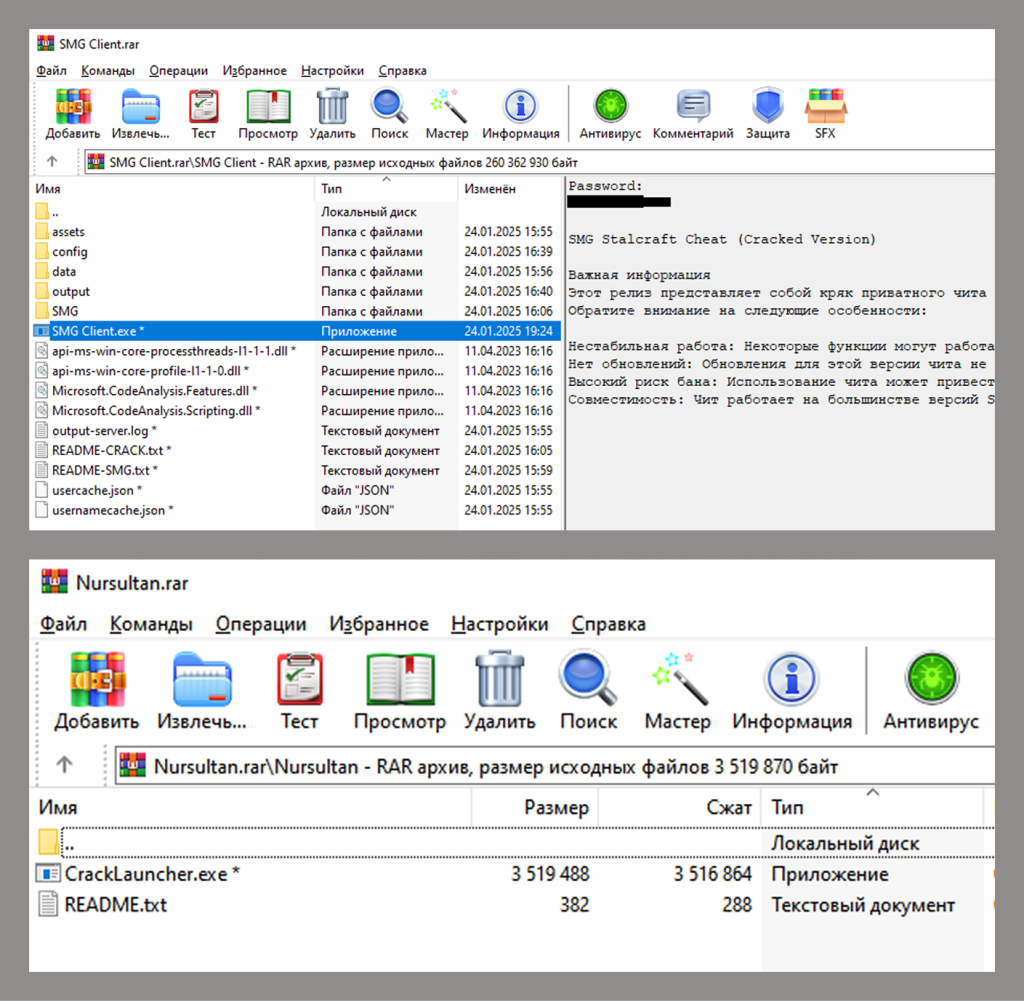
The DCRat backdoor is distributed through the YouTube platform. Attackers create fake accounts or use stolen ones, then upload videos advertising cheats, cracks, gaming bots and similar software. In the video description is a download link to the product supposedly being advertised. The link points to a legitimate file-sharing service where a password-protected archive awaits, the password for which is also in the video description.
Instead of gaming software, these archives contain the DCRat Trojan, along with various junk files and folders to distract the victim’s attention.
Backdoor
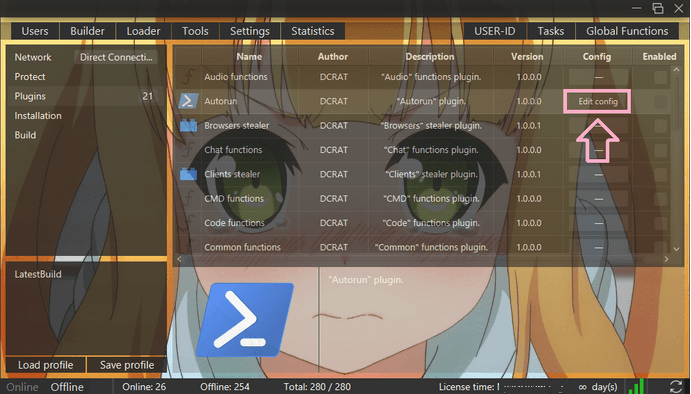
The distributed backdoor belongs to a family of remote access Trojans (RATs) dubbed Dark Crystal RAT (DCRat for short), known since 2018. Besides backdoor capability, the Trojan can load extra modules to boost its functionality. Throughout the backdoor’s existence, we have obtained and analyzed 34 different plugins, the most dangerous functions of which are keystroke logging, webcam access, file grabbing and password exfiltration.
Infrastructure
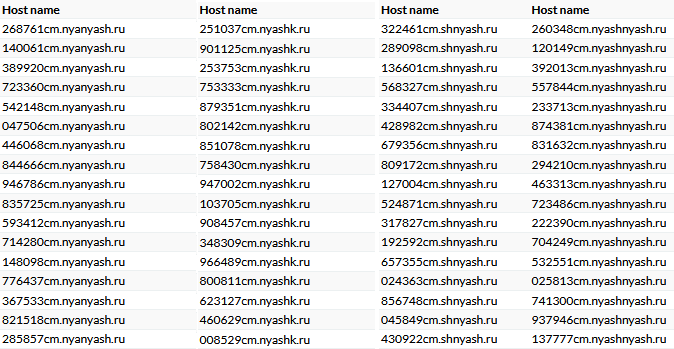
To support the infrastructure, the attackers register second-level domains (most often in the RU zone), which they use to create third-level domains for hosting the C2 servers. The group has registered at least 57 new second-level domains since the start of the year, five of which already serve more than 40 third-level domains.
A distinctive feature of the campaign is the appearance of certain words in the second-level domains of the malicious infrastructure, such as “nyashka”, “nyashkoon”, “nyashtyan”, etc. Users interested in Japanese pop culture will surely recognize these slang terms. Among anime and manga fans, “nyasha” has come to mean “cute” or “hon”, and it’s this word that’s most often seen in the second-level domains.
Victims
Based on our telemetry data since the beginning of 2025, 80% of DCRat samples using such domains as C2 servers were downloaded to the devices of users in Russia. The malware also affected a small number of users from Belarus, Kazakhstan and China.
Conclusion
Kaspersky products detect the above-described samples with the verdict Backdoor.MSIL.DCRat.
Note that we also encounter campaigns distributing other types of malware (stealers, miners, loaders) through password-protected archives, so we strongly recommend downloading game-related software only from trusted sources.
Original Post URL: https://securelist.com/new-wave-of-attacks-with-dcrat-backdoor-distributed-by-maas/115850/
Category & Tags: Research,Backdoor,Infrastructure,Malware,Malware Technologies,Malware-as-a-Service,RAT Trojan,YouTube,Windows malware – Research,Backdoor,Infrastructure,Malware,Malware Technologies,Malware-as-a-Service,RAT Trojan,YouTube,Windows malware
Views: 2