Source: securityaffairs.com – Author: Pierluigi Paganini
Experts warn that a new info-stealer named Statc Stealer is infecting Windows devices to steal a broad range of sensitive information.
Zscaler ThreatLabz researchers discovered a new information stealer malware, called Statc Stealer, that can steal a broad range of info from Windows devices.
The malware can steal sensitive information from various web browsers, including login data, cookies, web data, and preferences. The malicious code also targets cryptocurrency wallets and can capture credentials, passwords, and even data from messaging apps like Telegram.
Statc Stealer is written in C++, it supports filename discrepancy checks to avoid the execution in a sandbox and reverse engineering analysis.
The infection chain starts when victims are tricked into clicking on an ads that appears like an authentic Google advertisement.
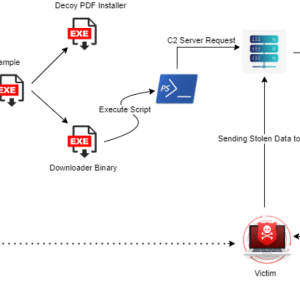
Below is the attack chain described by the researchers:
- A user is tricked into clicking on a malicious link somewhere on their Google Chrome browser (typically an advertisement).
- The user inadvertently downloads the Initial Sample file.
- After the malicious file executes, the Initial Sample drops and executes a Decoy PDF Installer.
- To facilitate the download of the Statc payload through a PowerShell script, the Initial Sample file also drops and executes a Downloader Binary file.
- Once Statc Stealer steals the user’s data, it encrypts the data, puts it in a text file, and stores it in the Temp folder.
- From here, Statc Stealer calls on its C&C server to deliver the stolen encrypted data.

The malware uses HTTPS the HTTPS protocol to send stolen, encrypted data to the C2 server.
The Statc Stealer targets most popular Windows browsers, including Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Brave, Opera, Yandex, and Mozilla Firefox.
Using ProcMon, the researchers observed that Statc Stealer can steal:
- user’s cookies data
- web data
- local state
- data preferences
- login data
- various different wallets information
- FileZilla
- browsers autofills
- anydesk
- ronin_edge
- meta mask
- Telegram data
The malicious code can also exfiltrate autofill data.
“In conclusion, the emergence of the new info stealer, Statc Stealer, highlights the relentless evolution of malicious software in the digital realm.” concludes the report. “Cybercriminals and their expanding list of malware types is becoming more complex by the minute. The discovery of Statc Stealer demonstrates the importance of staying alert, ongoing research, and monitoring.”
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, Statc Stealer)
Original Post URL: https://securityaffairs.com/149405/hacking/statc-stealer-info-stealer.html
Category & Tags: Breaking News,Hacking,Malware,Cybercrime,hacking news,info stealing malware,IT Information Security,malware,Pierluigi Paganini,Security Affairs,Statc Stealer – Breaking News,Hacking,Malware,Cybercrime,hacking news,info stealing malware,IT Information Security,malware,Pierluigi Paganini,Security Affairs,Statc Stealer
Views: 0